Zinc is a metal commonly used as an anodeit corrodes and gives up electrons to the steel. The below factors are considered during the Design phase.

Cathodic Protection Cathodic Protection Systems Matcor
An impressed current system consists of an external power source rectifier and anodes ground bed.

. Cathodic protection system the design of anode ground bed plays very important role since the current distribution and pipe potential will be affected by anode position with respect to the structure position. In the case of iron the oxides will be in the form of ferrous or ferric oxide. A groundbed is an electrode array that is installed beneath the ground to give off a path with low resistance to ground.
Most operators are faced with ground bed design issues due to environmental permitting and land acquisitionleasing difficulties. There are two types of cathodic protection. Locations for the groundbed and anode system.
DWD C31 Galvanic Cathodic Protection System Checkout DWD C32 Impressed Current Cathodic Protection System Checkout page 1 DWD C33 Impressed Current Cathodic Protection System Checkout page 2 DWD C34 Leak Repair Report Rev. CORROSION ENGINEER New England C P Inc. In terms of cathodic protection this groundbed refers to the anodes arrangement in water or ground which provides a way for protective currents out.
Passive cathodic protections work by attaching a metal anode which corrodes easier than the steel in the structure to be protected. Another 4 designs with anode rods arranged as 26 28 29 36 are calculated respectively. For underground structures requiring cathodic protection the location and nature of the site where the anode is placed needs careful considerationA low soil resistivity which would otherwise be classified as a highly corrosive soil is not the only factor which determines the location of the anodeOther factors to be considered include the presence of.
Corrosion is usually defined as the deterioration of a metal or its properties caused by a reaction with its environment. CATHODIC PROTECTION SYSTEM DESIGN Presented By DENIS L ROSSI PE. When exposed to oxygen and other oxidizing agents the refined metal will try to revert to its natural oxide state.
The results show that this design cannot meet the grounding resistance requirement. It is a vital component of the grounding system. A new CP ground-bed design compared with traditional design 27 14 anode rods dispersed in two parallel groups are calculated firstly.
Cathodic Protection Ground Beds. All the design and installation for cathodic protection system shall be in accordance with the latest edition of NACE standards NACE RP 0169. Impressed Current Cathodic Protection ICCP systems are known to many as the most widespread form of cathodic protection for pipelines.
The results show that this design can not meet the grounding resistance requirement. The different anode 2 Sacrificial anode cathodic protection SACP ground bed configurations that are generally installed may Sacrificial anode cathodic protection sacrifices one require more than one design to fully evaluate the efficacy metal referred to as the anode in order to protect a given and cost effectiveness of a design. 7deoh ri rqwhqwv qwurgxfwlrq 6wuxfwxuh.
We can provide unique and innovative design and installation. Determine the current. GROUND BED GB DESIGN.
Rectifiers have a vast array of other options most commonly in the following areas such as. CATHODIC PROTECTION DESIGN 21 Required information. The second concerns about the anode position effect on the cathodic protection system as well as the coating effect and the soil resistivity effectIn cathodic protection system the design of anode ground bed plays very important role since the current distribution and pipe potential will be affected by anode.
A new CP ground-bed design compared with traditional design 27 14 anode rods dispersed in two parallel groups are calculated firstly. Before deciding which type galvanic or impressed current cathodic protection system will be used and before the system is designed certain preliminary data must be gathered. We design and install Deep Well groundbed and anode systems to distribute impressed electrical current for cathodic protection against corrosion on steel pipelines underground storage tanks and oil and gas well casings.
At Point Integrity we have experience working with both galvanic and impressed current cathodic protection systems. What Does Groundbed Mean. Passive cathodic protection and impressed current cathodic protection ICCP.
For materials and equipment IEC code -. Cathodic Areas Anodic Area Pipe Wood Bed Block. A comparison have been made.
313 Anodes Ground Bed Specification 45. ScarredDamaged Surface Corrosion Threads scratches and dents are anodic to undisturbed surfaces along the pipe. Another 4 designs with anode rods arranged as 26 28 29 36 are calculated respectively.
211 Physical dimensions of.

Cathodic Protection Systems And The Nec Ec M
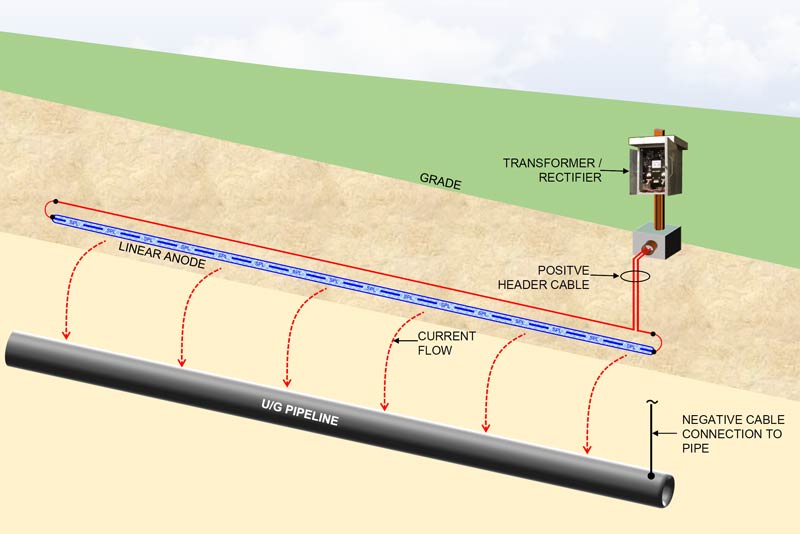
Shallow Horizontal Anode Bed Design With Linear Anodes Matcor Inc

Cathodic Protection Design Algorithms For Refineries Aboveground Storage Tanks Semantic Scholar

Cathodic Protection Definition Working Principles Types Design Advantages Applications Pdf What Is Piping
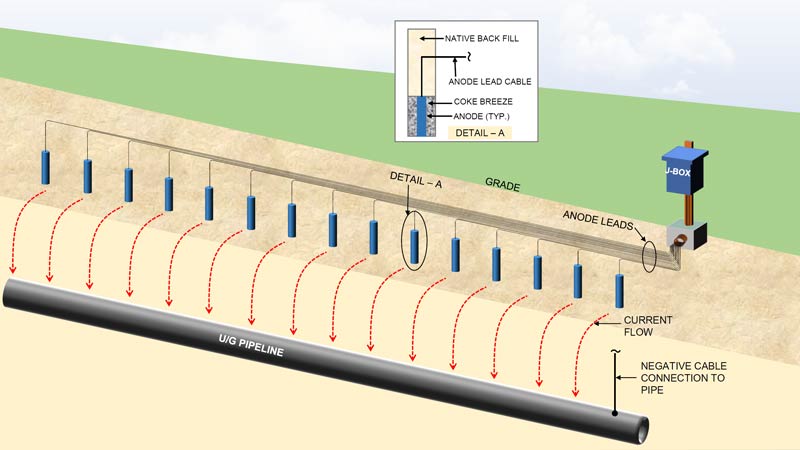
Shallow Horizontal Anode Bed Design With Linear Anodes Matcor Inc

Cathodic Protection Systems And The Nec Ec M

Schematic Design Of The Impressed Cathodic Protection Download Scientific Diagram

0 comments
Post a Comment